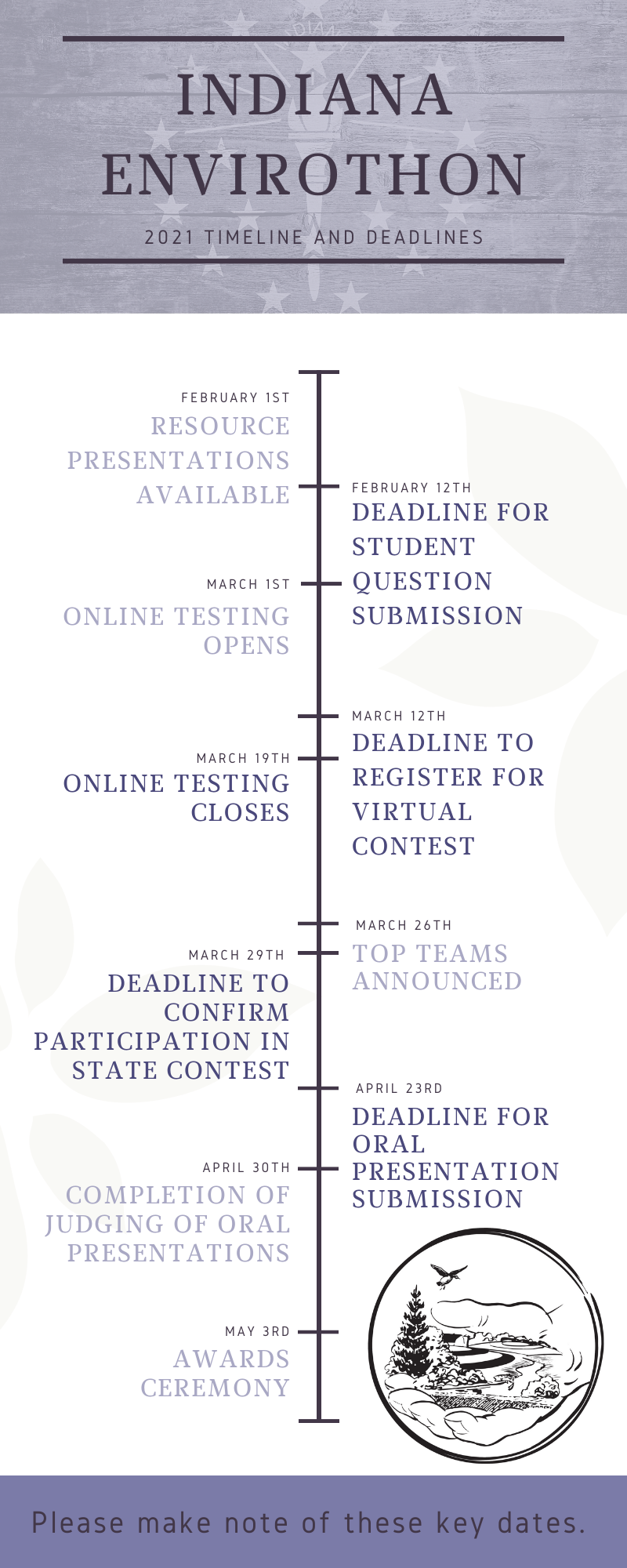
Central Indiana Regional EnvirothonGood News! The Envirothon has gone virtual and it is free this year. Regional Competition for the 2021 season is underway. Visit the new Indiana Envirothon website for registration and more information. The State Envirothon Committee has also decided to make the the Indiana State Envirothon completion virtual and free. Thanks you for your interest and continued focus on our Natural Resources.
For this years competition, teams will need to either complete the test virtually, with everyone in the testing room with access to a webcam or other video camera, or teams can meet in-person and obtain a proctor. Teams will still be tested together as a team, so think about scheduling some time with your teammates early. Contact our office for more information on proctoring guidelines.
Envirothon is a knowledge competition between teams of five students who represent various schools and organizations. Students must be in grades 9-12. Competitors will answer the provided questions based on aquatic ecology, forestry, soils/land use, wildlife, and the 2021 current issue which is Water Resources Management: Local Control and Local Solutions.
Students will be exposed to many new subjects as well as to various natural resources professionals. On the day of the competition, students will attend 5 short classes for each of the aforementioned subjects. There will be eight regional competitions in Indiana, and the top teams from each regional contest will then be invited to compete at the state level. The winner of the Indiana Envirothon will then compete this summer at the national NCF-Envirothon which will be held July 26th-August 1st, 2020 at the University of Nebraska Central Region Competition Date:
|
|
References - Visit the IndianaEnvirothon.org Website and click on the Resource Tab for the most up to date information- below are older resources that are still helpful
Information about the five topics can be studied through provided links below. Click on Subject Tab for a collection of references.
|
Hoosier Riverwatch
Volunteer Stream Monitoring Training Manual |
| ||
|
US Geological Survey (USGS) Water Resources
Only links provided are necessary |
The Water Cycle
Surface Water: Lakes & Reservoirs, Rivers, Rivers & the Landscape, Watersheds Groundwater: What is Groundwater, Aquifers |
|
Agencies Working on Clean Water
Be familiar with the agencies, programs, and roles of each. |
| ||
Aquatic Ecology Objectives
1. Identify assisting agencies and laws that govern Indiana waters, and develop a working understanding of the programs which benefit our water resources.
2. Define a watershed and the interaction of its components.
3. Define and understand the difference between non-point source and point source water pollution, as well as types of water pollution (organic, inorganic, thermal, toxic, etc.) and their impacts.
4. Be able to conduct water tests and interpret data for assessing water quality ie: dissolved oxygen, BOD5, turbidity, nitrate/nitrate etc.
5. Identify aquatic organisms, be able to classify them by pollution tolerance groups, and determine their indication of aquatic health.
6. Understand the unique characteristics of freshwater resources (lakes and ponds, rivers and streams, reservoirs, wetlands, and groundwater).
7. Understand the basic concepts of hydrology and the water cycle.
8. Be familiar with the distribution of the Earth’s water and understand water’s changing states and processes of the Water Cycle.
9. Be familiar with citizens' simple actions that can be implemented to prevent non-point source pollution.
10. Be able to identify and understand the interaction of segments of a community where water pollution may occur.
2. Define a watershed and the interaction of its components.
3. Define and understand the difference between non-point source and point source water pollution, as well as types of water pollution (organic, inorganic, thermal, toxic, etc.) and their impacts.
4. Be able to conduct water tests and interpret data for assessing water quality ie: dissolved oxygen, BOD5, turbidity, nitrate/nitrate etc.
5. Identify aquatic organisms, be able to classify them by pollution tolerance groups, and determine their indication of aquatic health.
6. Understand the unique characteristics of freshwater resources (lakes and ponds, rivers and streams, reservoirs, wetlands, and groundwater).
7. Understand the basic concepts of hydrology and the water cycle.
8. Be familiar with the distribution of the Earth’s water and understand water’s changing states and processes of the Water Cycle.
9. Be familiar with citizens' simple actions that can be implemented to prevent non-point source pollution.
10. Be able to identify and understand the interaction of segments of a community where water pollution may occur.
Past Links
|
Purdue Extension
FNR-180 (part 1 and 5 only), FNR-219, FNR-IDNR-36 |
Forestry Objectives
1. Know the parts of a tree and be able to explain the tree’s life cycle.
2. Identify common tree species without a key and identify specific or unusual trees & shrubs through the use of a key.
3. Understand the term silviculture and be able to explain the uses of the following silviculture techniques: thinning, prescribed burning, single tree & group tree selection, shelterwood method, clear-cutting with & without seed trees, & coppice management.
4. Know how to use forestry tools & equipment in order to measure tree diameter, height & basal area.
5. Understand how the following issues are affected by forest health & management: biodiversity, forest fragmentation, forest health, air quality, aesthetics, fire, global warming & recreation.
6. Understand how economic, social & ecological factors influence forest management decisions and policy affect sustainability.
7. Understand the economic value of forests and know many of the products they provide to people & society.
8. Know the typical forest structure: canopy, understory and ground layers and crown classes.
9. Understand forest ecology concepts and factors affecting them, including the relationship between soil and forest types, tree communities, regeneration, competition, and primary and secondary succession.
10. Understand what forestry best management practices (BMPs) are and how and why they are used to protect the forest and its soil and water resources while harvesting timber.
11. Understand the role of forests in protecting and enhancing water quality and that sustainable forest management is compatible with the protection of water resources.
2. Identify common tree species without a key and identify specific or unusual trees & shrubs through the use of a key.
3. Understand the term silviculture and be able to explain the uses of the following silviculture techniques: thinning, prescribed burning, single tree & group tree selection, shelterwood method, clear-cutting with & without seed trees, & coppice management.
4. Know how to use forestry tools & equipment in order to measure tree diameter, height & basal area.
5. Understand how the following issues are affected by forest health & management: biodiversity, forest fragmentation, forest health, air quality, aesthetics, fire, global warming & recreation.
6. Understand how economic, social & ecological factors influence forest management decisions and policy affect sustainability.
7. Understand the economic value of forests and know many of the products they provide to people & society.
8. Know the typical forest structure: canopy, understory and ground layers and crown classes.
9. Understand forest ecology concepts and factors affecting them, including the relationship between soil and forest types, tree communities, regeneration, competition, and primary and secondary succession.
10. Understand what forestry best management practices (BMPs) are and how and why they are used to protect the forest and its soil and water resources while harvesting timber.
11. Understand the role of forests in protecting and enhancing water quality and that sustainable forest management is compatible with the protection of water resources.
|
Soil Biology and Land Management (USDA)
|
| ||
Soils / Land Use Objectives
1. Identify partnering agencies and be aware of the programs that assist land users with soil issues.
2. Know and understand the 5 soil forming factors, their influence on soil properties, and the soil forming processes.
3. Know basic characteristics of the 12 soil taxonomic orders and know what soil orders are in Indiana.
4. Be able to recognize and identify features of soil profiles, properties, characteristics, structures, and be able to determine soil texture.
5. Recognize the importance of soil and that biological diversity is important for soil health and the health of those connected to the soil.
6. Understand the relationships of soil ecosystems as well as hydrologic, carbon, and nutrient cycles to soil management.
7. Understand that soil fertility relates to physical and chemical properties of the soil including quantity of nutrients essential for plants, and why it reflects the physical, chemical, and biological state of the soil.
8. Understand how different land uses and conservation practices impact soils and erosion, and the importance of soil management to agriculture/rural areas, urban environments, and to clean water, including point and non-point source pollution
9. Understand key terminology relating to soils and land use.
2. Know and understand the 5 soil forming factors, their influence on soil properties, and the soil forming processes.
3. Know basic characteristics of the 12 soil taxonomic orders and know what soil orders are in Indiana.
4. Be able to recognize and identify features of soil profiles, properties, characteristics, structures, and be able to determine soil texture.
5. Recognize the importance of soil and that biological diversity is important for soil health and the health of those connected to the soil.
6. Understand the relationships of soil ecosystems as well as hydrologic, carbon, and nutrient cycles to soil management.
7. Understand that soil fertility relates to physical and chemical properties of the soil including quantity of nutrients essential for plants, and why it reflects the physical, chemical, and biological state of the soil.
8. Understand how different land uses and conservation practices impact soils and erosion, and the importance of soil management to agriculture/rural areas, urban environments, and to clean water, including point and non-point source pollution
9. Understand key terminology relating to soils and land use.
Past Resources
|
Endangered Species Act (ESA) Basics
|
| ||
|
Animal Tracks of IN
(Please contact our office to inquire about loaning options) |
Animal Tracks of IN, Tamara Eder
Lone Pine Publishing, 2001, ISBN: 1-55105-307-1 |
|
American Wildlife & Plants: A Guide To Wildlife Food Habits
(Please contact our office to inquire about loaning options) |
Martin, Zim, Nelson: Dover Publications, Inc., 1951;
ISBN:0-486-20793-5 |
|
DNR Fish & Wildlife
Be familiar with the links and the info under About Us, Hunting Guide, 2018-2019 Seasons, Fishing Guide, Nongame & Endangered Wildlife, Nuisance Wildlife, Wildlife Resources, Wildlife Diseases, Animals, Invasive Species |
Wildlife Objectives
1. Understand the role of federal and state agencies, and the programs and laws that govern Indiana wildlife & the protection, conservation, management, and enhancement of Indiana’s wildlife & their habitat through improvement practices.
2. Identify Indiana wildlife species (mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, crustaceans, mussels, insects, spiders, etc.) by physical characteristics, tracks, movement patterns, habitat suitability, & other unique characteristic signs.
3. Identity and differentiate between extinct, extirpated, endangered, threatened, & species of special concern. Understand the importance of biodiversity and the implications of its loss. Describe factors affecting Indiana species and the methods being used to improve existing populations.
4. Describe the current struggles of native Indiana wildlife species impacted by biological & physical agents as well as the introduction of invasive non-native species & cite examples of current and potential concerns to native populations.
5. Identify basic wildlife survival needs of Indiana wildlife, the niche they serve, & habitats where they may be found. Describe specific adaptations of Indiana wildlife species to its environment and its role in the ecosystem.
6. Describe situations that limit or enhance population growth and discuss the concept of carrying capacity & limiting factors. Be familiar with examples that have or may occur in Indiana.
7. Be able to name habitat requirements for wildlife and the factors that affect suitability. Recognize the importance of wildlife adapting to its environment and be able to explain advantages of anatomical, physiological, and/or behavioral adaptations of wildlife to their environment.
8. Understand wildlife & wildlife related terminology such as: habitat, ecosystem, biodiversity, herbivore, endangered, food web, niche, invasive, etc.
9. Be familiar with current events that may be impacting Indiana wildlife, whether year-round residents or migratory species. (Due to how current the event there might not be a cited reference for this objective.)
2. Identify Indiana wildlife species (mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, crustaceans, mussels, insects, spiders, etc.) by physical characteristics, tracks, movement patterns, habitat suitability, & other unique characteristic signs.
3. Identity and differentiate between extinct, extirpated, endangered, threatened, & species of special concern. Understand the importance of biodiversity and the implications of its loss. Describe factors affecting Indiana species and the methods being used to improve existing populations.
4. Describe the current struggles of native Indiana wildlife species impacted by biological & physical agents as well as the introduction of invasive non-native species & cite examples of current and potential concerns to native populations.
5. Identify basic wildlife survival needs of Indiana wildlife, the niche they serve, & habitats where they may be found. Describe specific adaptations of Indiana wildlife species to its environment and its role in the ecosystem.
6. Describe situations that limit or enhance population growth and discuss the concept of carrying capacity & limiting factors. Be familiar with examples that have or may occur in Indiana.
7. Be able to name habitat requirements for wildlife and the factors that affect suitability. Recognize the importance of wildlife adapting to its environment and be able to explain advantages of anatomical, physiological, and/or behavioral adaptations of wildlife to their environment.
8. Understand wildlife & wildlife related terminology such as: habitat, ecosystem, biodiversity, herbivore, endangered, food web, niche, invasive, etc.
9. Be familiar with current events that may be impacting Indiana wildlife, whether year-round residents or migratory species. (Due to how current the event there might not be a cited reference for this objective.)
Past Resources
Water Resources Management: Local Control and Local Solutions
2020 Current Issue Objectives
1. Identify assisting agencies, tools, and laws that govern Indiana waters as a resource, and develop a working understanding of the programs which manage our water resources.
2. Be familiar with all components of a water budget, how they are monitored, and what part they play in a water budget.
3. Define and understand the process of integrated water management.
4. Understand the basic concepts of hydrology and the water cycle.
5. Knowledge of connection between groundwater and surface water, how they influence each other, and how human activities affect groundwater and surface water
6. Understand how to measure water availability and predict water use.
7. Understand how green infrastructure can manage water resources & the cost benefit process.
8. Define and describe Floodplain Protection, Impact of Floodway Construction Activities, National Flood Insurance Program and Flood Mitigation Programs.
9. Identify Indiana’s current knowledge of our water resources and what key elements will be needed to successfully manage our resources.
10. Discuss some surface water and groundwater best management practices used to help protect our water quality and quantity.
2. Be familiar with all components of a water budget, how they are monitored, and what part they play in a water budget.
3. Define and understand the process of integrated water management.
4. Understand the basic concepts of hydrology and the water cycle.
5. Knowledge of connection between groundwater and surface water, how they influence each other, and how human activities affect groundwater and surface water
6. Understand how to measure water availability and predict water use.
7. Understand how green infrastructure can manage water resources & the cost benefit process.
8. Define and describe Floodplain Protection, Impact of Floodway Construction Activities, National Flood Insurance Program and Flood Mitigation Programs.
9. Identify Indiana’s current knowledge of our water resources and what key elements will be needed to successfully manage our resources.
10. Discuss some surface water and groundwater best management practices used to help protect our water quality and quantity.
More Study Tools